FAQ’s on Regenerative Medicine and Seattle Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cells are the foundation cells for our bodies. They act as a “blank slate” and differentiate into specialized cells that make up all of our tissues and organs. As a person forms and develops, he/she continuously replenishes stem cells that are used to repair injured tissues.
Stem cells are defined by: their ability to self-renew and divide and their ability to differentiate into more specialized cells that make up the organs and tissues. These specialized cells can be injected into damaged and injured body regions. Stem cells are plentiful in amniotic fluid, which is what is used at R3 Stem Cell centers after processing at an FDA regulated facility.
What are the various types of stem cells?
There are many kinds of stem cells. These include:
- Embryonic stem cells – These cells exist in the earliest stages of development. They can be grown during fetal development and are quite valuable for regenerative medicine. These cells will differentiate into many cell types. Embryonic stem cells are used to test new drugs and replace injured tissues and damaged organs. These are NOT used in treatment at our centers. No fetal tissue is used and babies are not harmed in any way.
- Tissue-specific (adult stem cells) – Appear during fetal development and remain throughout life in the body. These cells are multipotent, which means that can convert into most different mature cell types, such as muscle, skin, tendon, intestine, etc. Various tissues contain these stem cells that replace cells and restore tissue after injury.
- Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS cells) – Created in the laboratory and not found in other areas of the body. iPS cells are non-pluripotent, which means they can transform into any cell type found in the body. These cells are reprogrammed to an unspecialized state, and they hold promise for creating disease-specific cell lines, which are used for research. These are commonly being used in Asia, but not in the US.
What is regenerative medicine?
The goal of regenerative medicine is to repair tissues or organs damaged by aging, trauma, and disease. Regenerative medicine allows function of tissues to be improved or restored. In the past, treatments for degenerative conditions consisted of “band aid” options that have helped with symptoms such as pain, but haven’t actually changed anything.
Regenerative medicine, on the other hand, helps to alter conditions by repair and regeneration, rather than the “band aid”. It’s been a revolutionary advancement!
What diseases and conditions are treated with stem cell therapy?
Stem cells may help treat:
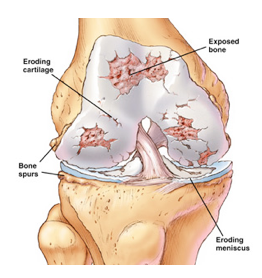
- Arthritis – Stem cell therapy is being used to rebuild damaged cartilage, which erodes away from osteoarthritis. The regenerative materials help to repair damaged soft tissues from arthritis and help individuals walk better and get back to desired activities.
- Sports Injuries – elite and amateur athletes are now undergoing stem cell procedures frequently. The procedures have helped many athletes prolong their careers, avoid surgery and get back into their sport quickly!
- Back and Neck Pain– either due to arthritis or degenerative disc disease. Studies are showing it works excellent.
- Soft Tissue Injury – Tendonitis, Bursitis, Ligament Injury, Fasciitis
- Diabetes – For people with type 1 diabetes stem cells may help.
- Heart disease – Research is being conducted to evaluate if or not heart muscle can be repaired using stem cells.
- Parkinson’s disease – Studies have shown that stem cells may help.
- Alzheimer’s disease – Stem cells have been shown to improve memory loss, behavioral problems, and cognitive decline.
- Lou Gehrig’s disease – Also called amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), this disease may be improved with stem cells. Scientists have been exploring developing motor neurons with stem cells.
- Lung diseases – Researchers in the US are exploring use of stem cells to replace damaged lung cells. For patients with COPD, the regenerative treatments are working exceptionally well.
Do stem cell injections work?
Several studies show that stem cells work well for various conditions. This includes musculoskeletal conditions such as arthritis, sports injuries, and overuse conditions.
Examples include degenerative arthritis, cartilage defects, tendonitis, COPD, kidney disease, post-stroke and more.
The various treatment procedures being used at our Seattle stem cell therapy clinics are:





